What can be more frustrating than a slow-loading website at the most important moment of the movie; or a stuttering video; or lagging data sharing? Probably nothing.
According to research, Internet users find slow-loading websites the most annoying and terrifying thing compared to other issues. Such a poor performance results in overall customer dissatisfaction, and thus, business failures. When the speed of content sharing is in the focus, CDNs come into play.
CDN is a smart solution that brings content closer to the user, thus, accelerating the speed of the website and improving the overall performance of the service provider. Let’s explore what the CDNs are, how they speed up website performance, and how businesses can benefit from them.
What is CDN (Content Delivery Network)?
A content delivery network is a group of interconnected servers located worldwide. They are created to cache the website’s content (images, documents, downloads, videos) and deliver the copy to the end user faster. Put simply, the CDNs are the data centers that are located close to the end user, which automatically speeds up the website’s performance.
Let’s imagine Netflix, a global streaming service hosted in California, USA. An average US citizen will reach the data within seconds, yet, a transatlantic user in Finland should wait much longer for the data to be delivered. Instead, Netflix exploits the CDN located closer to Finland, which keeps the cached copies of the data. Thus, Finnish viewers will enjoy the same quality of performance as the users of ‘native’ servers. Global CDN providers like Gcore, for example, are available in 180+ points of presence with a network capacity of over 200 terabits per second (Tbps).
The CDN handles the requests faster than the host server located at a distance, thus, providing much faster data sharing. As a result, the users receive the quality and speed they are expecting, while businesses get relevant financial benefits.
How Can Businesses Benefit from CDN?
CDN is a powerful solution for every business targeting global extensions in content delivery. Considering an ever-increasing level of competition, staying ahead of others is the key to success; CDN seems to be the basic solution.
- Accelerated website performance
CDNs allow businesses to distribute the cached content globally, thus, the users get a highly responsive website and quickly load the website.
Such a performance makes a world of difference compared to remote host servers and the time spent on data retrieval.
- Unlimited website scalability
The usage of CDNs allows the unloading of the host servers from sudden spikes in user activity, thus, preventing performance failures.
- Risk aversion
CDNs perform as data backups. In case the host website features technical issues and shuts down, the CDN will keep providing users with relevant data, thus, maintaining proper uptime and uninterrupted user experience.
- Enhanced security
CDNs are an advanced solution, well-protected against cyberattacks. They protect host servers by absorbing’ all the hackers’ attacks.
- Cost saving
CDN is a financially efficient solution to distribute the content, as instead of running an extensive number of original servers, the business simply benefits from hosting and infrastructure service by paying particular fees.
Also Read: What You Should Know When Migrating from MySQL 5.7 to 8.0
Types of CDNs
CDNs can support both static and dynamic types of content:
- Static content
Static content, as the name suggests, features non-changeable content, which is always delivered in the same form to the users. Usually, it is related to the small portfolio website with images, documents, videos, and HTML files.
- Dynamic content
Pages with dynamic content feature constant changes depending on the user, location, time of visit, and type of interaction. For instance, social media, online shopping, streaming services, etc.
Unlike static content, dynamic is based on real-time user requests and is scripted in the origin server.
The new generation of CDNs can run the script inside the edge servers, and thus, generate the content according to the user’s needs.
Types of CDNs
There are two types of CDNs:
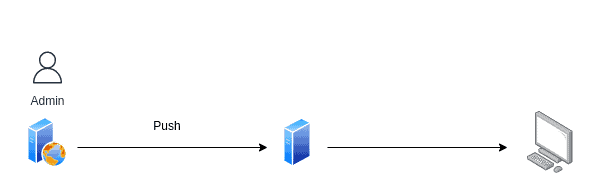
- Push CDN
The website owner ‘pushes’ (sends) all the content to CDN and is responsible for managing and updating the stored content.
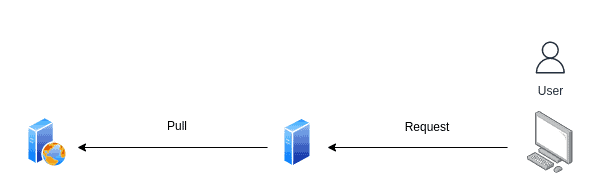
2. Pull CDN
The CDN servers ‘pull’ (retrieve) the content from the origin server automatically based on user requests.
While both pull and push CDNs work well for the websites, there is a small difference:
- Pull CDN is more suitable for websites that get a lot of traffic due to relatively constant content. It is ideal for small files like website images, JavaScript scripts, CSS files, and HTML files.
- Push CDN is a better fit for websites with little traffic as the content is pushed to the server once and remains unchanged. It is used for content larger than 10 MB.
The Final Thoughts
Today’s world is powered by content of different kinds and the speed of its delivery. CDN is a reliable and cost-effective solution that helps to deliver content to an end-user without losing its quality and minimizes time-to-user content delivery. The network stores readily available content in a required format and sends it to the user once requested. Such responsiveness makes websites more popular with users and increases the financial benefits for every business involved.